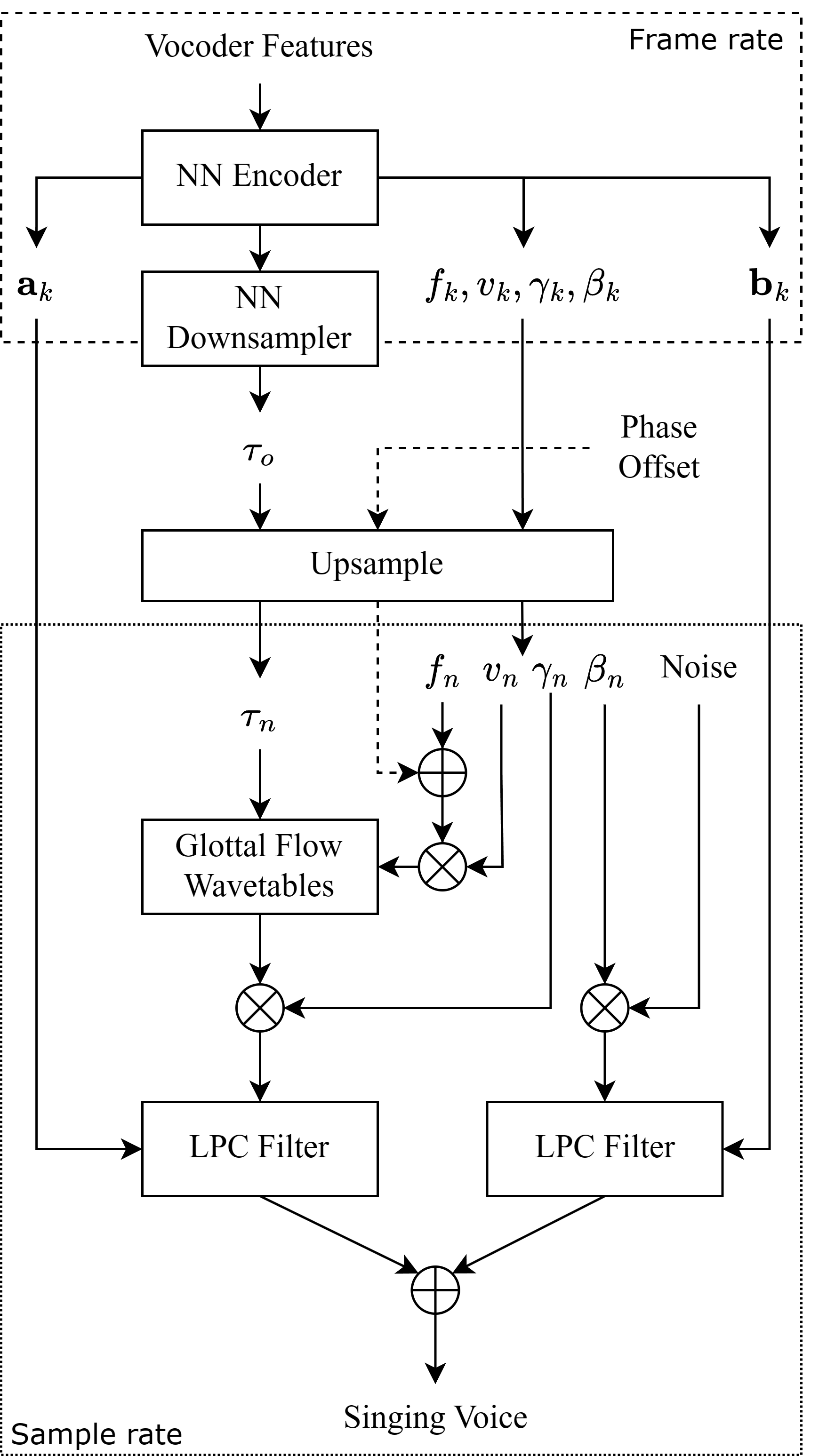
Abstract
This paper introduces GlOttal-flow LPC Filter (GOLF), a novel method for singing voice synthesis (SVS) that exploits the physical characteristics of the human voice using differentiable digital signal processing. GOLF employs a glottal model as the harmonic source and IIR filters to simulate the vocal tract, resulting in an interpretable and efficient approach. We show it is competitive with state-of-the-art singing voice vocoders, requiring fewer synthesis parameters and less memory to train, and runs an order of magnitude faster for inference. Additionally, we demonstrate that GOLF can model the phase components of the human voice, which has immense potential for rendering and analysing singing voices in a differentiable manner. Our results highlight the effectiveness of incorporating the physical properties of the human voice mechanism into SVS and underscore the advantages of signal-processing-based approaches, which offer greater interpretability and efficiency in synthesis.
Listening Samples
This section contains the listening samples used for subjective evaluation in the paper. Reference is the ground truth audio, and the other columns are the synthesized audio from different models. The synthesis paraemters were computed from the ground truth mel-spectrograms.
Singer f1
| Test clip | Reference | DDSP | SawSing | PULF | GOLF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clip 1 | |||||
| Clip 2 | |||||
| Clip 3 |
Singer m1
| Test clip | Reference | DDSP | SawSing | PULF | GOLF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clip 1 | |||||
| Clip 2 | |||||
| Clip 3 |
Additional Materials
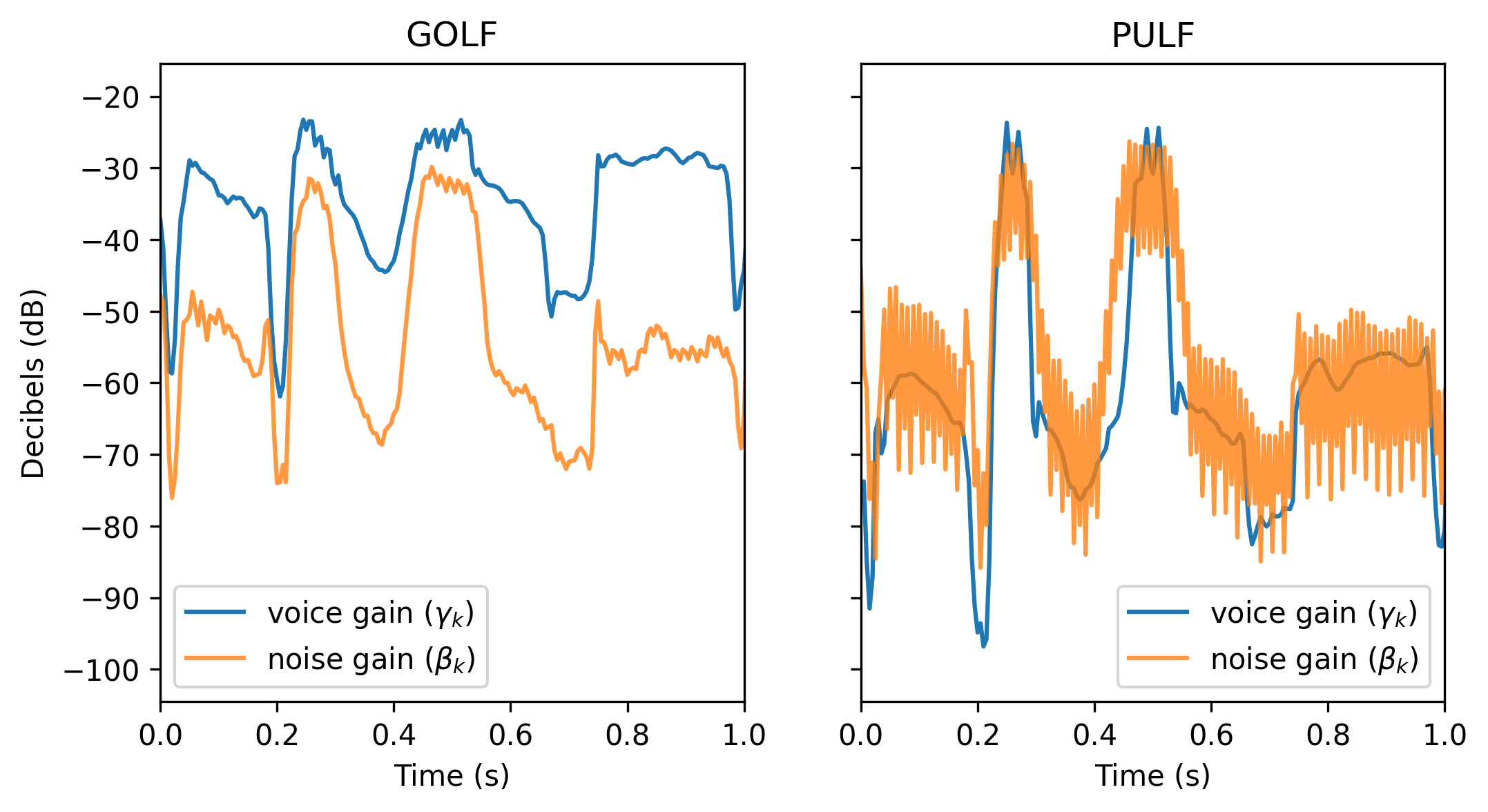
Fluctuation Artefacts
The following image illustrates the fluctuation artefacts mentioned in the discussions section of the paper, using one second of audio from the f1 test samples. The noise gain predicted by PULF is fluctuating at a high speed. Other parameters also show similar behavior but the effect is small. We hypothesise the cause could relate to:
- The spectral energy distributions of the harmonic components.
- The errors introduced by the frame-wise LPC approximation.
Decompositions
We show the intermediate representations of f1 clip 1 from GOLF.
| Representation | Audio | Spectrogram |
|---|---|---|
| Predicted pitch (pulse train) |
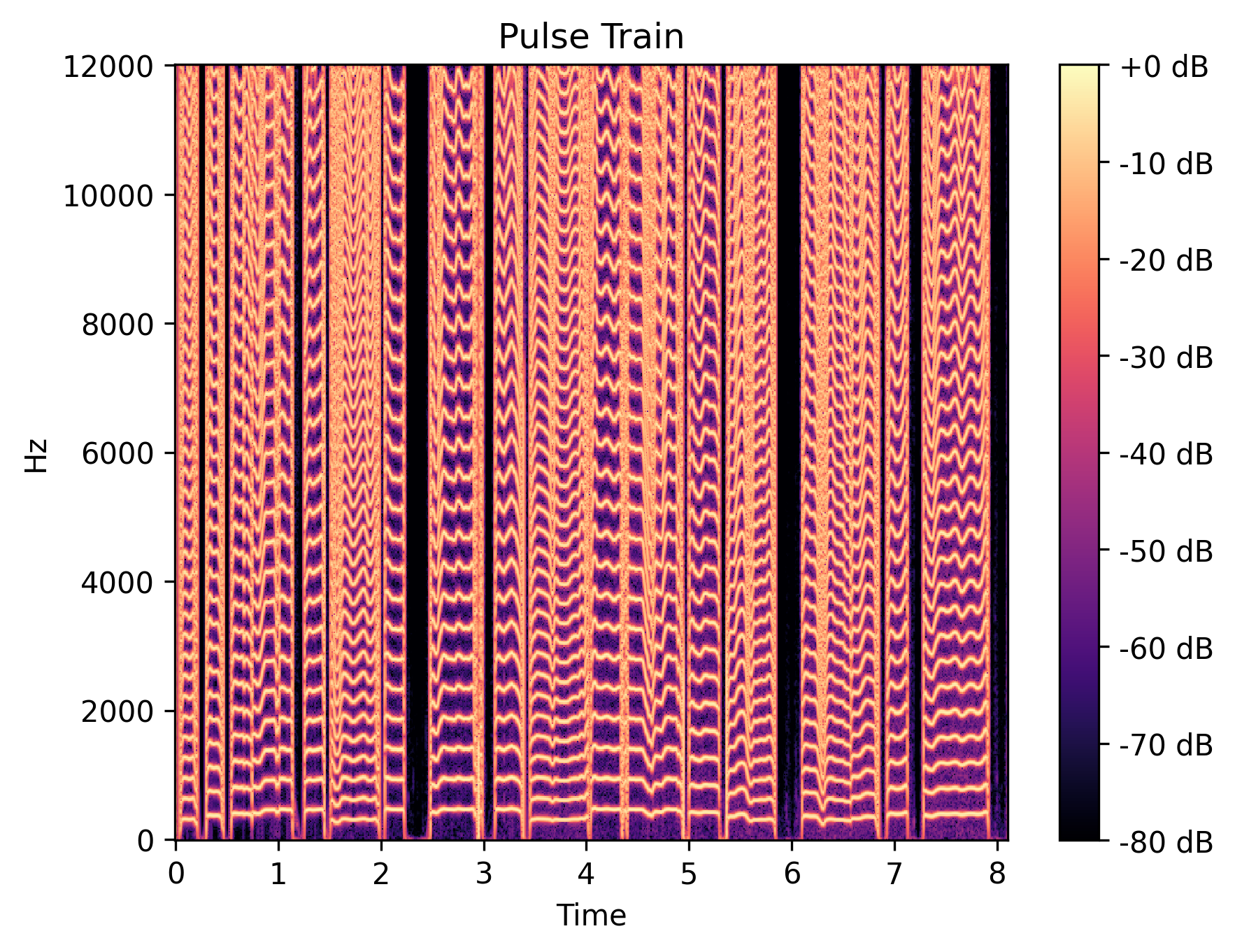
|
|
| Glottal flow |
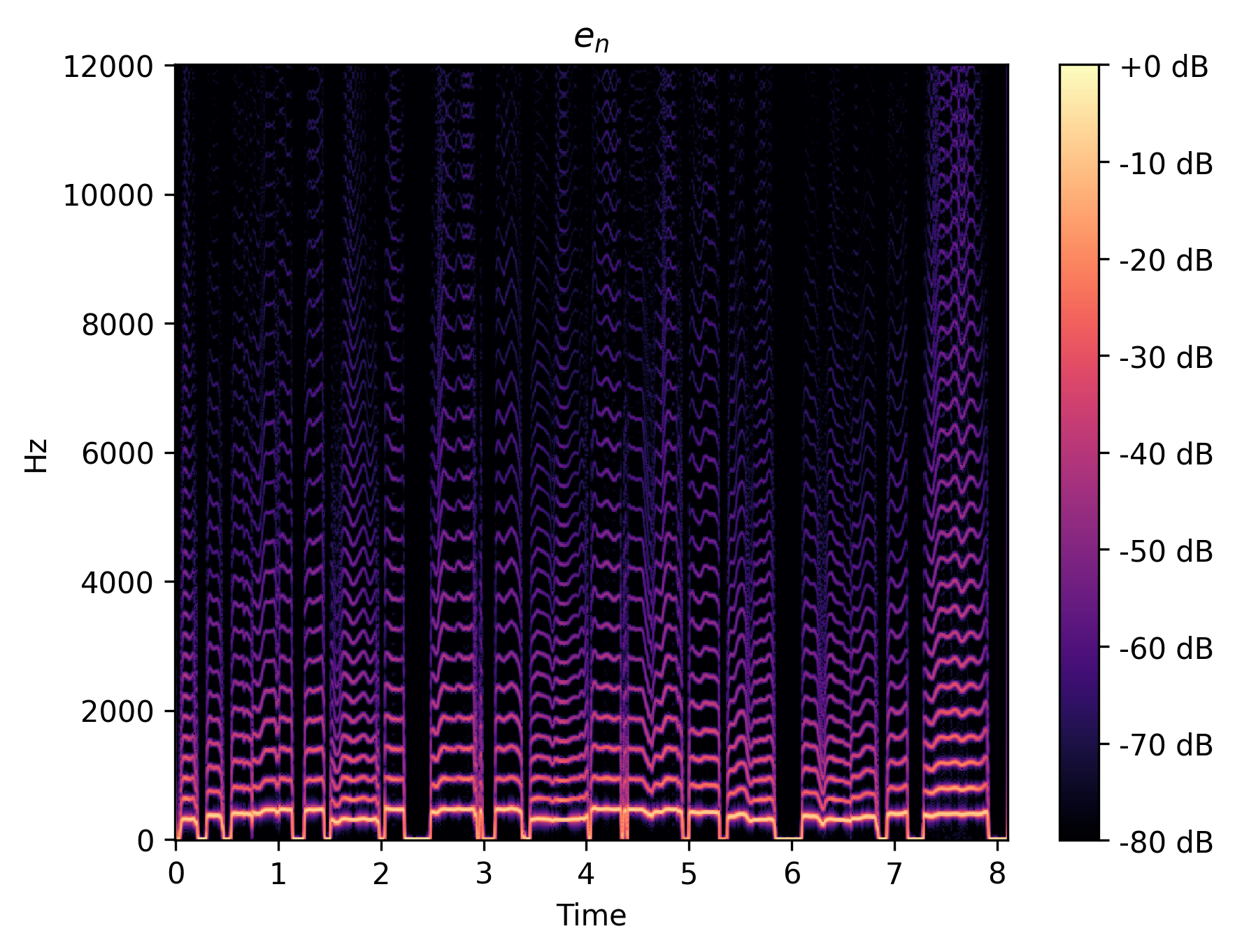
|
|
| Filtered glottal flow |
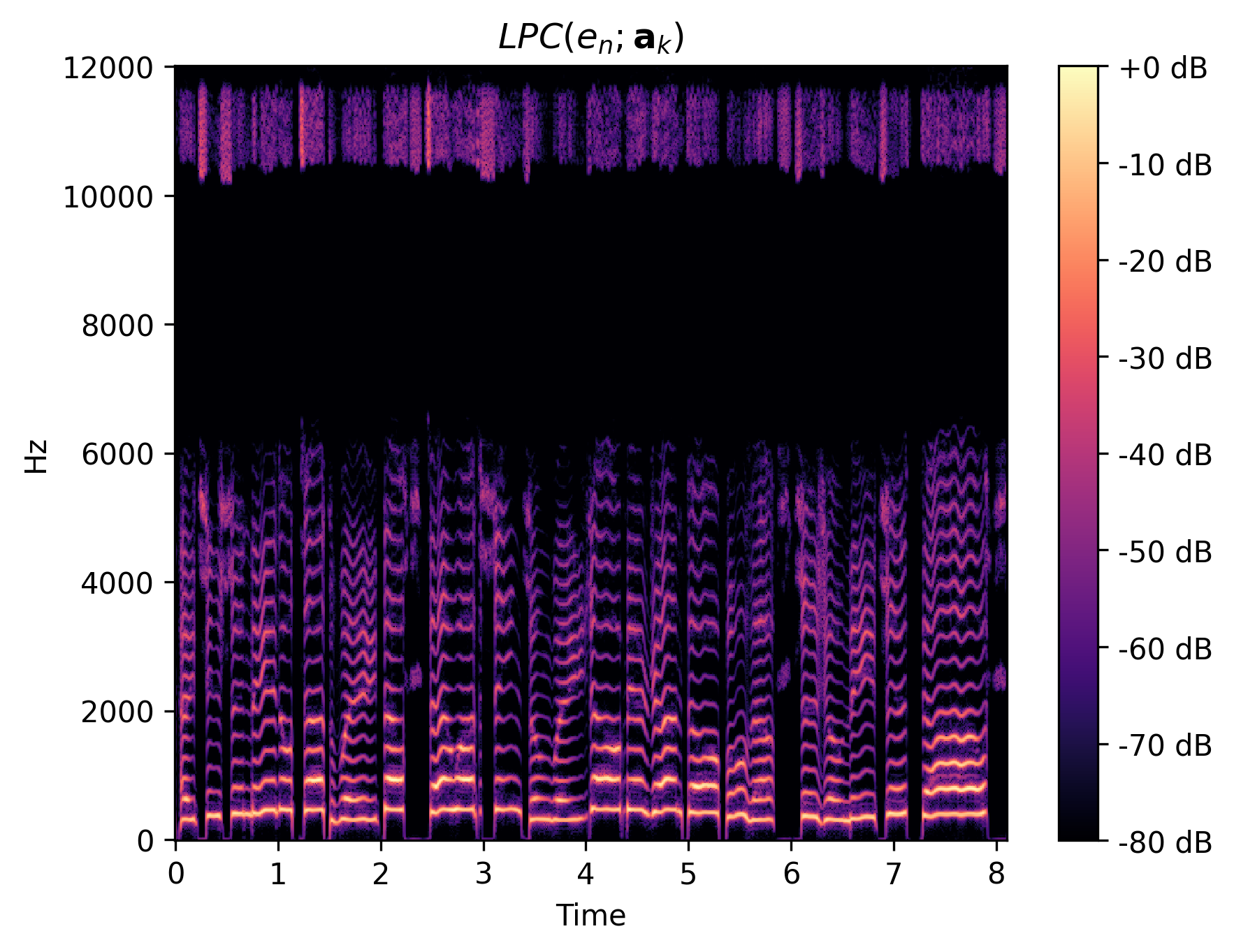
|
|
| Residual |
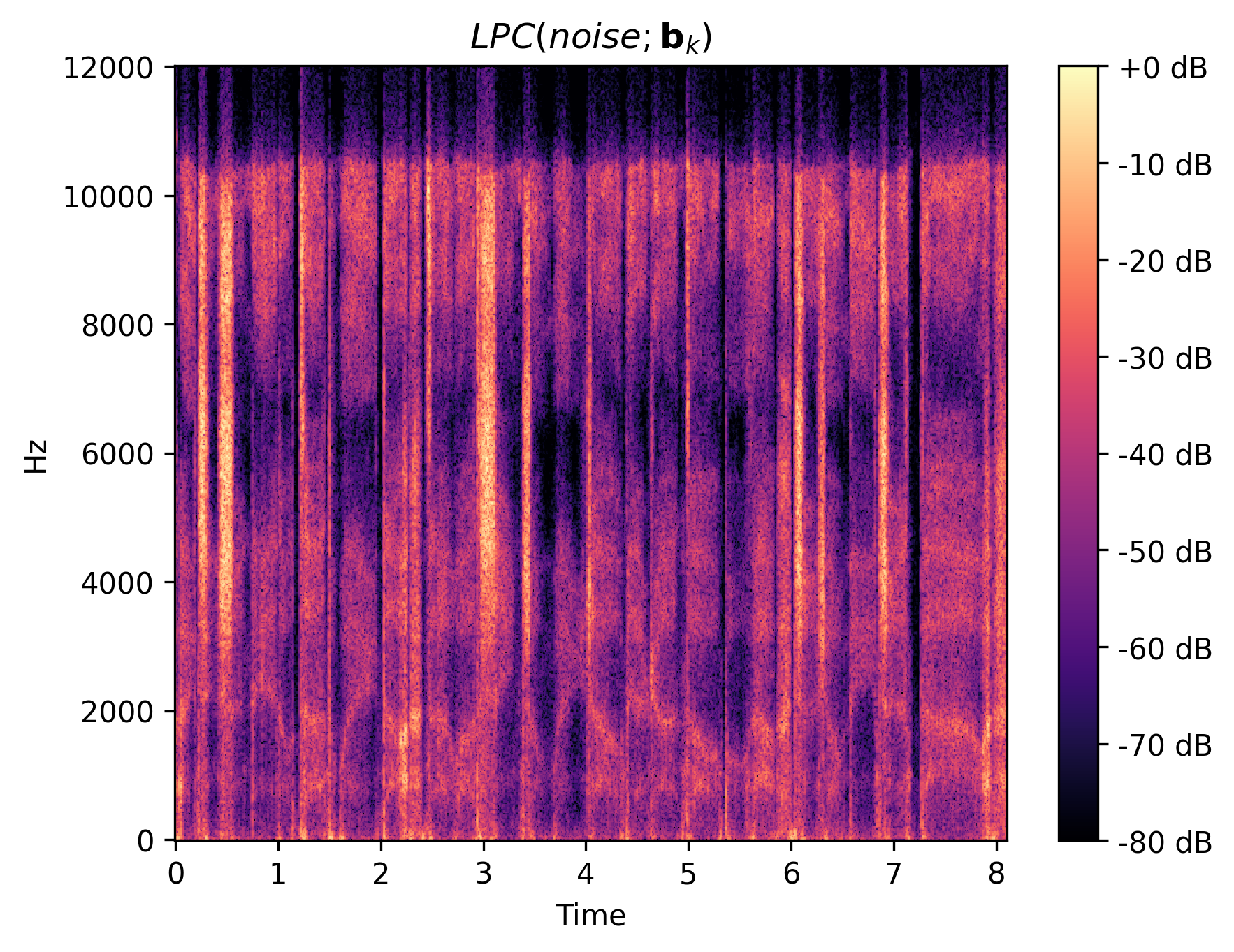
|
|
| Combined |
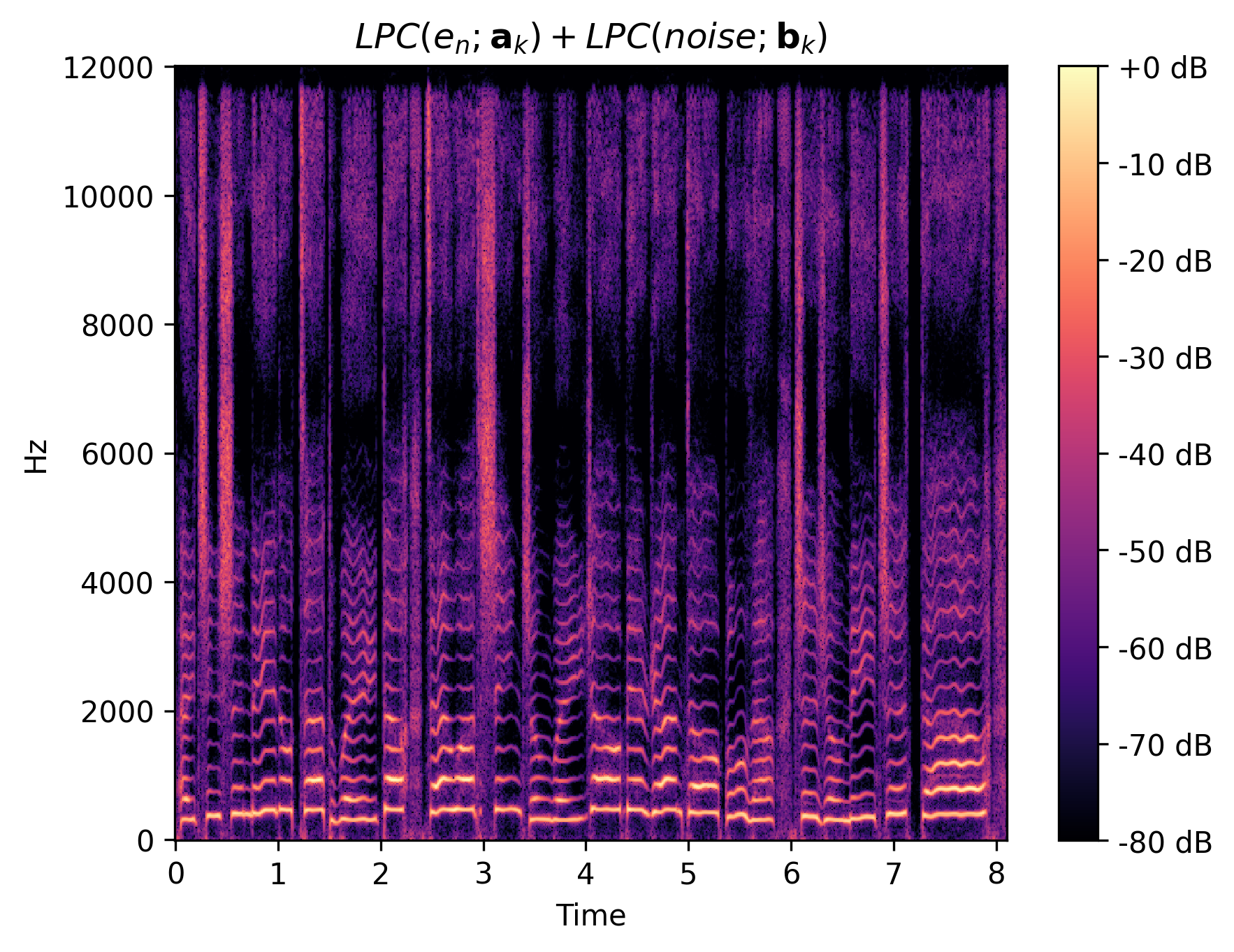
|
|
| Original |
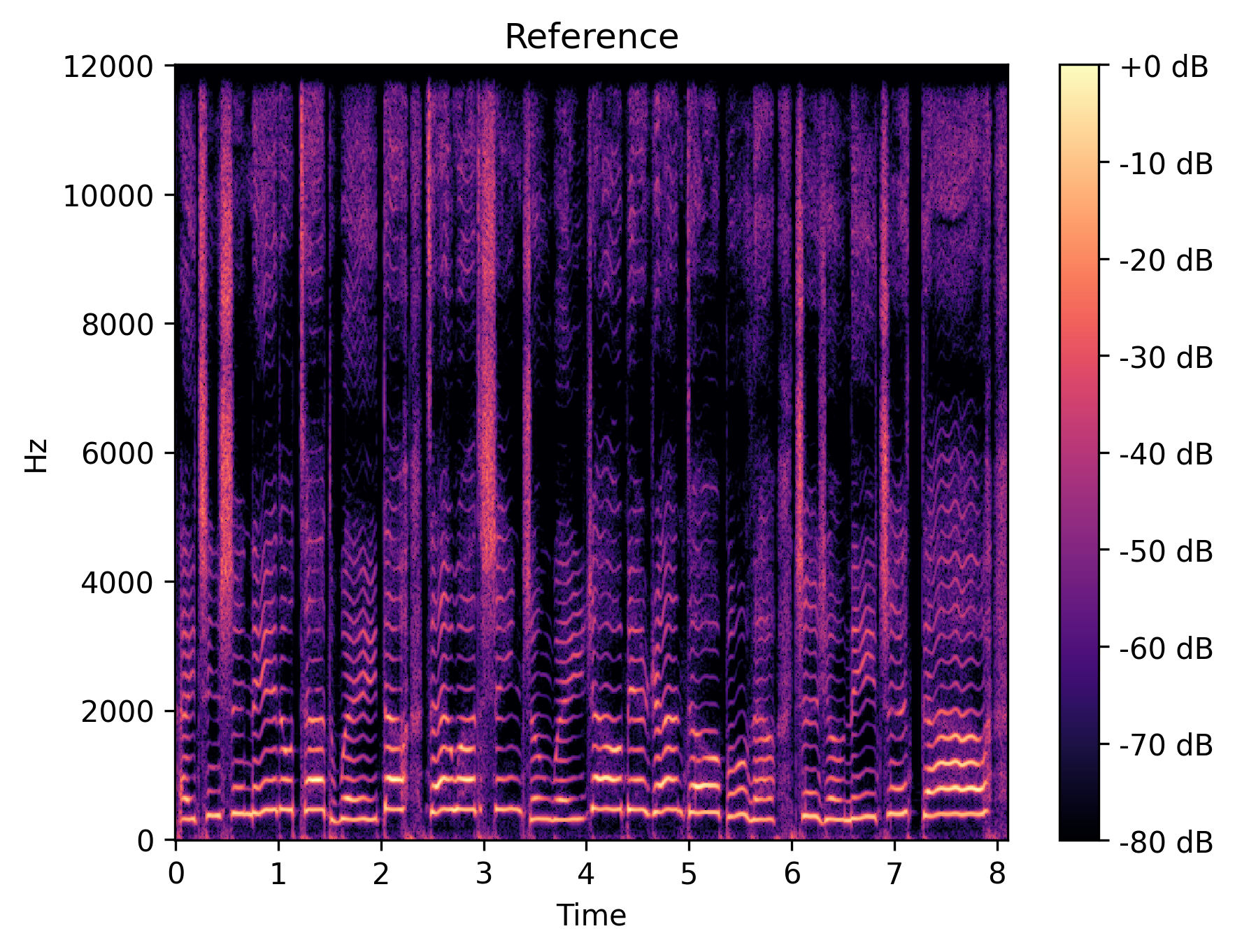
|
Citation
@inproceedings{ycy2023golf,
title={Singing Voice Synthesis Using Differentiable LPC and Glottal-Flow-Inspired Wavetables},
author={Chin-Yun Yu and Gy{\"o}rgy Fazekas},
booktitle={International Society for Music Information Retrieval (ISMIR)},
year={2023}
}